- Copper-base Brazing Plate Heat Exchanger
- Nickel-base Brazing Plete Heat Exchanger
- Rubber pad sealed Plate Heat Exchanger
Copper-base Brazing Plate Heat Exchanger is composed of a set of corrugated pipe plates between the front and rear baffle plates. The baffle assembly is composed of a sealing plate, a sealing ring and a baffle plate. The interface type can be customized according to the market and application domain requirements. In vacuum brazing, a weld is formed at each point of contact between the sheet and the filler material (brazing solder). Using this design, it is possible to make a heat exchanger composed of two different channels or circuits.
A: According to customer needs, the production layout is divided into:
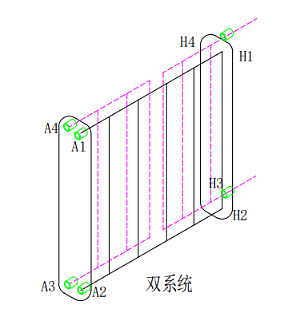
Two-system brazing heat exchanger (Picture 1)
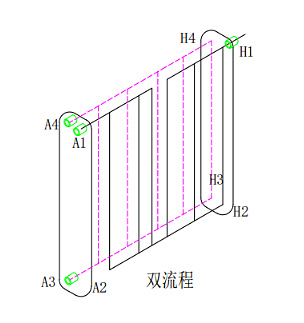
Two-flow brazing heat exchanger (Picture 2)
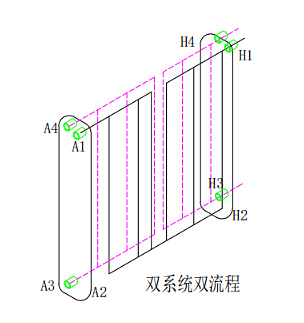
Dual-system dual-process brazing heat exchanger (Picture 3)
B: According to the Angle of the hermitage, it can be divided into:
H channel has high heat transfer coefficient and high resistance. Suitable for small flow but strong heat transfer (high specific heat, phase change or large temperature difference), such as refrigerant phase change heat transfer.
L channel has low heat transfer coefficient and low resistance. It is suitable for large flow and weak heat transfer (low specific heat or small temperature difference), such as air heat transfer under ambient pressure.
Compared with Copper-base Brazing Plate Heat Exchanger, the solder has changed, there is no copper element, the product can be used in food and medical industries.
Nickel-base Brazing Plete Heat Exchanger is composed of a set of corrugated pipe plates between the front and back plates. The interface type can be customized according to the market and application domain requirements. In vacuum brazing, a weld is formed at each point of contact between the sheet and the filler material (brazing solder). Using this design, it is possible to make a heat exchanger composed of two different channels or circuits.
A: According to customer needs, the production layout is divided into:

Dual system Nickel-base Brazing Plete Heat Exchanger (Picture 1)

Dual flow Nickel-base Brazing Plete Heat Exchanger (Picture 2)

Dual system dual flow Nickel-base Brazing Plete Heat Exchanger (Picture 3)
B: According to the Angle of the hermitage, it can be divided into:
H channel has high heat transfer coefficient and high resistance. Suitable for small flow but strong heat transfer (high specific heat, phase change or large temperature difference), such as refrigerant phase change heat transfer.
L channel has low heat transfer coefficient and low resistance. It is suitable for large flow and weak heat transfer (low specific heat or small temperature difference), such as air heat transfer under ambient pressure.
Plate heat exchanger is a heat exchanger made of thin metal plate pressed into a certain corrugated shape, and then stacked, with splint, bolt fastening. Thin rectangular channels are formed between various plates through which heat is exchanged. The working fluid flows through a narrow, winding channel formed between the two plates. The hot and cold fluids pass through the flow passage successively, and there is a partition plate in the middle to separate the fluids, and the heat transfer is carried out through the plate.
The structure and heat transfer principle of plate heat exchanger determine that it has the characteristics of compact structure, small area, high heat transfer efficiency, large operational flexibility, wide application range, small heat loss, convenient installation and cleaning.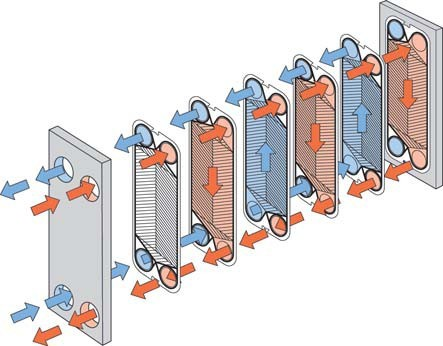
water hammer test, salt spray test, blasting test, cold and hot alternating, water, oil pressure and other professional testing experiments.
of flux-free joints. Advantages of vacuum welding: Avoid oxidation caused by flux, no cleaning after welding, minimize residual stress and deformation, no heat affected zone.